
Future Of Climate Change Global Impacts And Survival Solutions
The future of climate change is no longer a distant concern—it is unfolding right now. Human activities like burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial expansion have accelerated long-term shifts in global temperatures and weather patterns. As we move deeper into the 21st century, these changes are becoming more intense, frequent, and disruptive.
While the situation is serious, it is not hopeless. By understanding the global impacts of climate change and focusing on practical survival solutions, humanity can still adapt, protect vulnerable communities, and reduce future risks.
Global Impacts of Climate Change
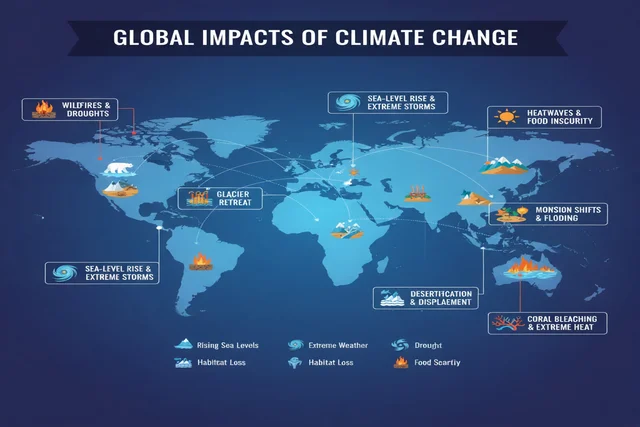
Climate change is affecting every region of the world, but not in the same way. Some impacts are sudden and visible, while others build slowly and quietly, reshaping societies over time.
1. Rising Global Temperatures
The most direct and measurable impact of climate change is rising global temperatures. Scientists warn that crossing the 1.5°C threshold increases the risk of irreversible damage to ecosystems and human health.
By 2030 and beyond, heatwaves are expected to become longer and more intense. In some regions, especially parts of South Asia, the Middle East, and Africa, summer heat could reach levels that make outdoor work and daily life increasingly dangerous.
2. Melting Ice and Sea-Level Rise
As global temperatures rise, glaciers and polar ice sheets are melting faster than scientists previously predicted. This melting contributes directly to sea-level rise, putting coastal cities and island nations at risk, according to NASA’s latest sea-level data.
Low-lying cities like New York, Mumbai, and Jakarta, along with coastal regions around the world, are facing flooding, saltwater intrusion, and severe damage to infrastructure. For millions of people, this could mean forced migration and long-term displacement.
3. Extreme Weather Events
The future climate is expected to produce more extreme and unpredictable weather. Hurricanes are becoming stronger due to warmer ocean temperatures, while rainfall patterns are shifting dramatically.
Some regions are experiencing devastating floods, while others face prolonged droughts that dry up rivers, destroy crops, and strain water supplies. These extremes increase food prices, disrupt economies, and place immense pressure on emergency systems.
4. Loss of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Collapse
Climate change is happening faster than many species can adapt. As temperatures rise and habitats shift, plants and animals are disappearing at alarming rates. Coral reefs are bleaching, forests are shrinking, and pollinators like bees are declining.
This loss of biodiversity weakens ecosystems that humans rely on for food, clean water, and climate stability. When nature breaks down, human survival becomes more uncertain.
5. Water Scarcity and Climate Migration
Freshwater availability is becoming one of the most serious challenges of the future. Melting glaciers initially boost water flow, but over time they reduce long-term supplies. At the same time, droughts are drying up reservoirs and depleting groundwater sources.
As water and food grow scarce, climate-driven migration is increasing. Communities are being forced to leave their homes, creating social, economic, and political pressures across entire regions.
Survival Solutions: How Humanity Can Adapt

To secure a livable future, climate action must focus on two key areas: mitigation, which reduces the causes of climate change, and adaptation, which helps societies adjust to unavoidable impacts.
1. Transition to Renewable Energy
Moving away from coal, oil, and gas is one of the most important survival strategies. Expanding solar, wind, and green hydrogen energy reduces emissions while creating more resilient energy systems.
Organizations such as the International Energy Agency (IEA) closely track global progress in clean energy transitions, showing that meaningful change is possible when strong policies align with smart investments.
2. Climate-Resilient Infrastructure
Future cities must withstand extreme heat, floods, and storms through smarter design. This means building better drainage systems, constructing flood-resistant buildings, installing sea walls in high-risk areas, and using heat-reflective materials in urban planning.
Climate-resilient infrastructure not only protects lives but also helps reduce long-term economic losses.
3. Sustainable and Climate-Smart Agriculture
Climate change is putting global food systems under increasing pressure through heatwaves, droughts, floods, and shifting growing seasons. Climate-smart agriculture focuses on farming methods that help crops survive these stresses while maintaining productivity. It aims to reduce agriculture’s carbon footprint while improving soil health, water efficiency, and long-term resilience in both small and large farming systems.
This approach includes the use of drought- and heat-resistant crop varieties, precision irrigation to limit water waste, and regenerative practices such as crop rotation and improved soil management. By strengthening food security and protecting farmers’ livelihoods, climate-smart agriculture plays a critical role in helping societies adapt to climate change while reducing future environmental risks.
4. Nature-Based Solutions and Reforestation
Nature-based solutions use natural ecosystems to address climate challenges while delivering benefits for people and biodiversity. Protecting forests, restoring wetlands, and expanding urban green spaces help absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and reduce rising temperatures. These ecosystems also act as natural buffers against floods, heatwaves, and soil erosion, making communities more resilient to climate impacts.
Reforestation and ecosystem restoration strengthen climate adaptation by rebuilding degraded landscapes and supporting wildlife habitats. When managed responsibly, these efforts improve air quality, regulate water cycles, and provide long-term climate protection. Investing in nature-based solutions allows societies to work with nature, rather than against it, to secure a more stable and sustainable future.
5. Smarter Water Management
Freshwater is becoming one of the most precious resources in a warming world. Rising temperatures, shifting rainfall patterns, and melting glaciers are putting immense pressure on rivers, lakes, and groundwater supplies. Efficient water management is now essential for both agriculture and daily life, ensuring that communities can continue to access safe and sufficient water.
Modern solutions such as desalination to turn seawater into usable freshwater, recycling wastewater, and collecting rainwater for irrigation and domestic use. On a personal level, simple actions like conserving water at home, fixing leaks, and using efficient irrigation systems help reduce demand and ensure sustainable use. Effective water management protects communities from scarcity while supporting food security and climate resilience.
The Role of Technology and AI
Technology is playing an increasingly vital role in tackling climate change. In 2025, artificial intelligence and advanced data systems are helping predict weather patterns, optimize energy use, and monitor environmental changes in real time. Satellites and sensors track temperature shifts, water availability, and ecosystem health, enabling faster and more precise decision-making.
From AI-driven energy grids to early-warning systems for extreme weather, technology helps communities adapt and respond more effectively. It also supports innovations in agriculture, renewable energy, and urban planning, bridging the gap between scientific research and practical climate solutions. By leveraging technology responsibly, societies can strengthen resilience and reduce the impacts of global warming.
Personal Actions: What Can You Do?
While governments and corporations must lead large-scale change, individual actions still matter. Reducing waste, improving energy efficiency at home, and supporting climate-focused policies all contribute to collective impact.
Small choices, when multiplied across millions of people, can drive meaningful change.
The future of climate change represents one of the greatest challenges humanity has ever faced. Rising temperatures, sea-level rise, biodiversity loss, and water scarcity are reshaping the world we live in.
Yet, survival solutions exist. Through renewable energy, climate-resilient planning, nature-based approaches, and global cooperation, we can reduce risks and protect future generations. The window for action is narrowing, but it remains open. What we do today will define the climate future of tomorrow.
Read more related articles: https://www.climatechallange.com/oceans-in-crisis-2025-the-reality-of-1-5c-global-warming/
FAQs
Q1: Is climate change still reversible?
Ans. Some impacts are already locked in, but the worst outcomes are not inevitable. Rapid emission reductions and adaptation efforts can still prevent extreme scenarios and protect future generations.
Q2: How will climate change affect daily life in the future?
Ans. People may face higher food prices, water shortages, extreme heat, and more frequent disasters. These changes will influence health, work, and living conditions worldwide.
Q3: Which regions are most vulnerable to climate change?
Ans. Coastal areas, small island nations, and parts of the Global South face the highest risks. However, no region is completely safe from climate impacts.